 Yellowstone Caldera Chronicles is a weekly column written by scientists and collaborators of the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory. This week's contribution is from Annie Carlson, Research Coordinator at the Yellowstone Center for Resources, Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone Caldera Chronicles is a weekly column written by scientists and collaborators of the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory. This week's contribution is from Annie Carlson, Research Coordinator at the Yellowstone Center for Resources, Yellowstone National Park
Parks are for the people.
As the first national park, Yellowstone was established in 1872 as a “pleasuring-ground for the benefit and enjoyment of the people.” The National Park Service is tasked with both protecting park resources and providing for their enjoyment. To accomplish this dual mission, some infrastructure is necessary to support high levels of visitation. But how much infrastructure is appropriate?
How do you allow people to enjoy their parks without damaging resources? These questions continue to be a central focus for park managers, and our opinion of what is appropriate has changed over time. The Upper Geyser Basin, home of beloved Old Faithful Geyser, is a great place to ponder these changing attitudes.
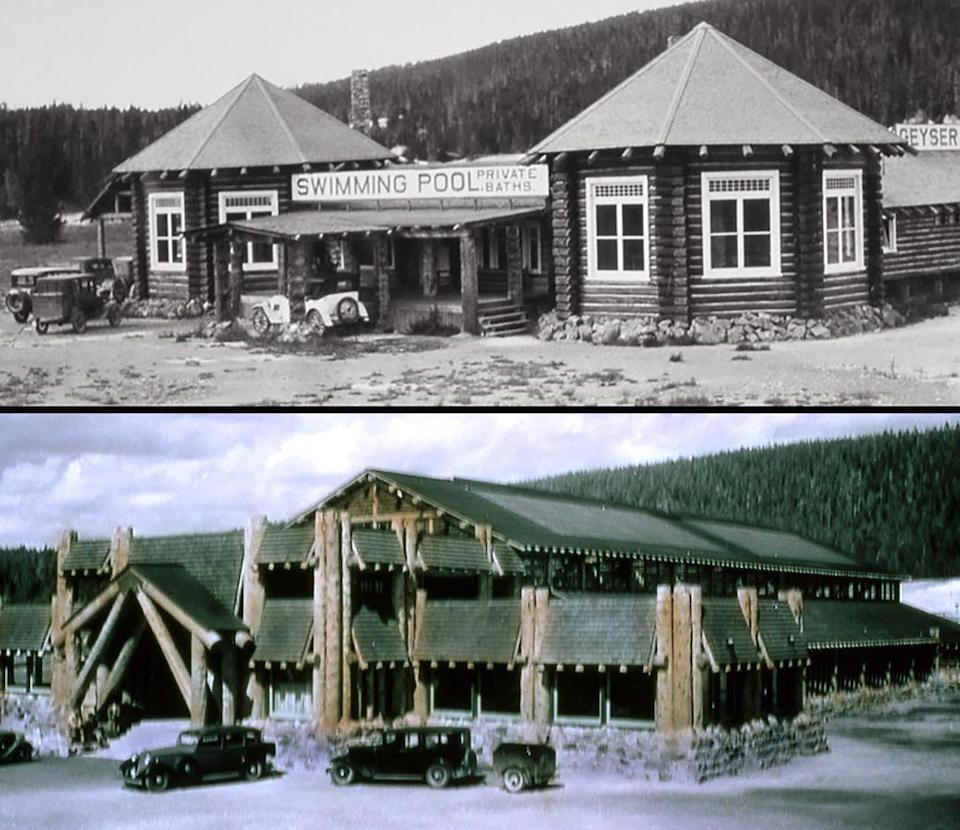
Since the early days of the park, the Upper Geyser Basin has been one of the most popular areas for Yellowstone visitors. Today, you’ll find large parking lots, three hotels, two general stores, two gas stations, a visitor center, and a system of trails and boardwalks to safely navigate the thermal area.
But what you see today is only a snapshot of the infrastructure that has been there since the 1870s. In the past, structures have included tent camps, a bear-feeding platform, a thermally heated greenhouse, and even a hot-water swimming pool!
As you can imagine, decades of piping hot water changed Solitary Geyser’s natural behavior. When the Brothers pool was built, they dredged and deepened the outlet channel. They also built wooden cooling frames to move the water downhill. The lowered water level in the spring allowed boiling to occur at depth, and Solitary Geyser began regular eruptive behavior.

Hot water was piped from Solitary Geyser to the former site of the geyser bathhouse.
Even though the water level has been restored since the bathhouse closed, Solitary continues to have regular geyser eruptions. You are likely to catch an eruption if you wait for 5-10 minutes, although most are only about 3 feet high.




Comments
There was also a swimming pool at the Roosevelt Camp before my time in 1959and 1960, but the empty remains of the pool were still in place at that time. Do not know when the pool was originally constructed or closed down.
Hi Larry: do you remember where it was? I'm writing a book about the employee experience and the pool is referred to in 1924. I'm guessing it's near Lost Creek but not sure how far in.